Reverse engineering is a powerful tool we use to help clients bring their product ideas to life more efficiently. By breaking down existing designs, we uncover valuable insights that drive innovation and improvements. This approach enables us to replicate intricate components, understand complex mechanisms, and even revive legacy products when original parts are unavailable. For our clients, reverse engineering shortens the product development timeline, reduces costs, and ensures precise replication of critical designs. Whether we’re enhancing a competitor’s product or recreating obsolete parts, our reverse engineering process plays a vital role in delivering quick, effective solutions. In this blog, we’ll explore the key benefits of reverse engineering, the industries that rely on it, and how it shapes modern product development. You’ll see how reverse engineering allows for rapid innovation, supports legacy systems, and creates better products for our clients.
What Does Reverse Engineering Mean?
Reverse engineering is the process of taking apart an existing product to understand how it works. Instead of creating a new design from scratch, engineers deconstruct a product to gain insights into its construction and operation. The purpose of reverse engineering is to replicate, improve, or analyze a product’s design and functionality. By examining the structure, materials, and assembly, engineers can uncover the product’s inner workings and identify areas for improvement or innovation. Reverse engineering can help companies recreate outdated components, understand competitor products, or develop more efficient versions of existing designs.
What Industries Use Reverse Engineering?
Reverse engineering is widely used across many industries, especially those dealing with complex products or highly specialized components.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturers often rely on reverse engineering to improve processes, replace obsolete parts, or replicate competitor designs for market comparison.
- Automotive: The automotive industry uses reverse engineering to analyze competitor vehicle components, understand material properties, and improve design features for safety or efficiency.
- Aerospace: In the aerospace industry, reverse engineering helps engineers reconstruct components of older aircraft, especially when original parts are no longer available.
- Medical Devices: Reverse engineering assists in developing or improving medical devices, where precise replication is critical for patient safety and performance.
- Electronics: The electronics industry uses reverse engineering to analyze circuit boards, identify technological gaps, and recreate complex systems for study or improvement.
- Defense: Reverse engineering is vital in the defense sector, helping to improve weapon systems or adapt enemy technology.
What Tools Are Used in Reverse Engineering?
Reverse engineering uses several advanced tools and technologies to gather and process data. These tools allow engineers to create accurate models of physical products, replicate their functionality, and understand their design.
- 3D Scanners: 3D scanning technology captures the physical dimensions of an object and creates a digital model. Laser or structured-light scanners are used to map out the exact shape, size, and surface details of the product.
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Software: CAD software helps engineers reconstruct the scanned data into a detailed digital model. It allows them to modify or enhance the design based on the captured data.
- Disassembly Tools: Engineers use various hand tools to carefully dismantle a product without damaging any critical parts. These tools help analyze the internal structure and assembly methods.
- Measurement Tools: Precision measurement tools, like calipers and micrometers, are used to measure exact dimensions of smaller components. This ensures that the product can be replicated or improved with high accuracy.
- Material Analyzers: Material analyzers determine the exact materials used in a product. Understanding the material composition is essential for recreating the product or finding suitable alternatives.
- Finite Element Analysis (FEA) Software: FEA software helps engineers study how a product will respond to forces such as heat, vibration, and pressure. It provides insights into the product’s durability and helps identify potential failure points.
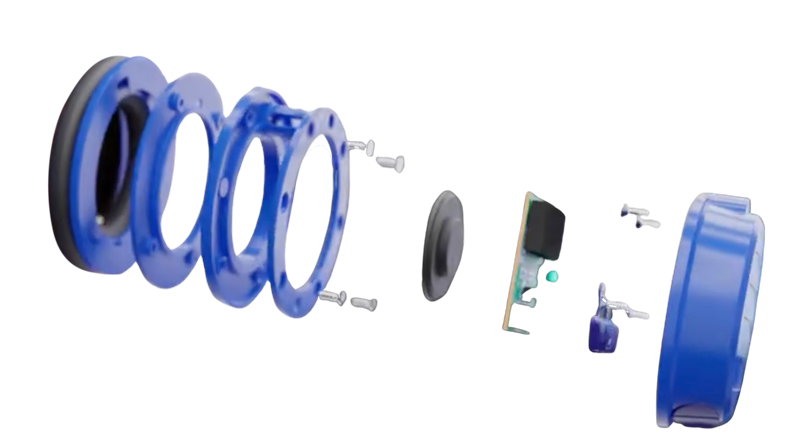
Why is it important?
Reverse engineering plays a crucial role in modern product development. Its importance stems from its ability to drive innovation, improve existing designs, and extend the lifespan of older products. By understanding how something works, engineers can make it better, more efficient, or more cost-effective. Reverse engineering also allows companies to bring new products to market faster by analyzing competitors’ designs or enhancing outdated ones. When original designs are unavailable, reverse engineering can provide valuable information for recreating essential components, ensuring the continued functionality of machines or systems.
The Top 5 Benefits of Reverse Engineering
1. Allows for Rapid Innovation
Reverse engineering accelerates innovation by providing a starting point for product development. Instead of building from the ground up, engineers can take existing products, learn from them, and identify improvements. This method saves time and helps companies bring improved products to market faster. By examining a competitor’s product, engineers can introduce superior features or address flaws more quickly. Reverse engineering encourages creative solutions and better products by leveraging existing knowledge.
2. Shortens the Product Development Process
Starting with a detailed understanding of a competitor’s product, reverse engineering eliminates the need to spend excessive time on research and prototyping. This process significantly reduces the development time, allowing companies to create products faster. The insights gained from reverse engineering can guide the development team, providing a roadmap to optimize the design or improve functionality. As a result, the time between concept and market release is shortened, enabling businesses to stay ahead in competitive industries.
3. Can Replicate Intricate Shapes
Many products have intricate or complex geometries that are difficult to recreate through traditional design methods. Reverse engineering, particularly when combined with 3D scanning technology, allows for precise replication of even the most complex shapes. The scanner captures every detail, and the data is translated into digital models that can be modified or recreated. This benefit is especially useful in industries like aerospace and medical devices, where precision and accuracy are critical for safety and performance.
4. Can Help You Understand Existing Products
Reverse engineering offers a detailed understanding of a product’s design, materials, and assembly. By breaking down the product, engineers can identify its strengths and weaknesses, revealing ways to improve its functionality, performance, or cost-effectiveness. This process helps businesses understand why certain design choices were made, allowing them to make informed decisions when developing their products. It also aids in discovering flaws or inefficiencies in competitor products, creating opportunities for improvement.
5. Legacy Product Support
Many industries rely on products or systems that are decades old and no longer supported by the original manufacturer. Reverse engineering allows engineers to recreate parts or components for these legacy systems, ensuring their continued operation. This is especially important in industries like aerospace and defense, where replacing entire systems is costly and impractical. By reverse engineering components, companies can keep older systems functional without the need for expensive replacements or upgrades.
How Useful Is Reverse Engineering?
Reverse engineering proves to be highly useful in many contexts. It helps companies stay competitive by allowing them to quickly replicate or improve on existing products. Whether it’s reverse engineering a competitor’s product to gain an edge or recreating a critical component for an obsolete system, this process provides a practical and efficient way to drive innovation. In industries that rely on precise designs and performance, reverse engineering ensures products meet the required standards and continue to function as intended. For legacy product support, reverse engineering extends the life of systems that might otherwise become obsolete, saving significant costs.
What Is the Main Goal of Reverse Engineering?
The primary goal of reverse engineering is to understand a product’s design, structure, and functionality. By gaining insight into how a product works, companies can improve it, replicate it, or create something new based on its framework. Reverse engineering aims to analyze and interpret the existing design to provide a foundation for innovation or replication. Whether the goal is to create more efficient designs, solve manufacturing challenges, or study competitors’ products, reverse engineering provides the tools and knowledge needed to achieve those objectives.
What Type of Projects Require Reverse Engineering?
Reverse engineering is essential for a variety of projects, especially those involving complex or obsolete designs. Projects that require precise replication, such as medical devices or aerospace components, often depend on reverse engineering to ensure accuracy and functionality. When original blueprints are unavailable or when systems are too old to find replacement parts, reverse engineering provides a way to recreate those critical components. It is also used in product improvement projects, where engineers analyze existing products to identify flaws, introduce enhancements, or reduce manufacturing costs. Additionally, reverse engineering helps companies studying competitors’ products to improve upon existing designs or introduce new features that set their products apart.
Lime Design's Approach to Perfecting Product Development

In the realm of product development, there is an art to embracing failure as a catalyst for growth and improvement. Lime Design, a leading product development firm, has mastered the art of failing forward, using it as a powerful tool to uncover and refine imperfections in the journey of bringing an inventor’s idea to life. By understanding the value of iteration and actively seeking out failures, Lime Design’s team is able to transform setbacks into stepping stones towards creating exceptional products. In this blog, we delve into Lime Design’s unique approach and how they harness the art of failing forward to perfect the development process.
Transform your idea into a product! Don’t tackle the hurdles of product development alone. Partner with our experienced team to navigate the process seamlessly. Reach out today to start turning your vision into reality!