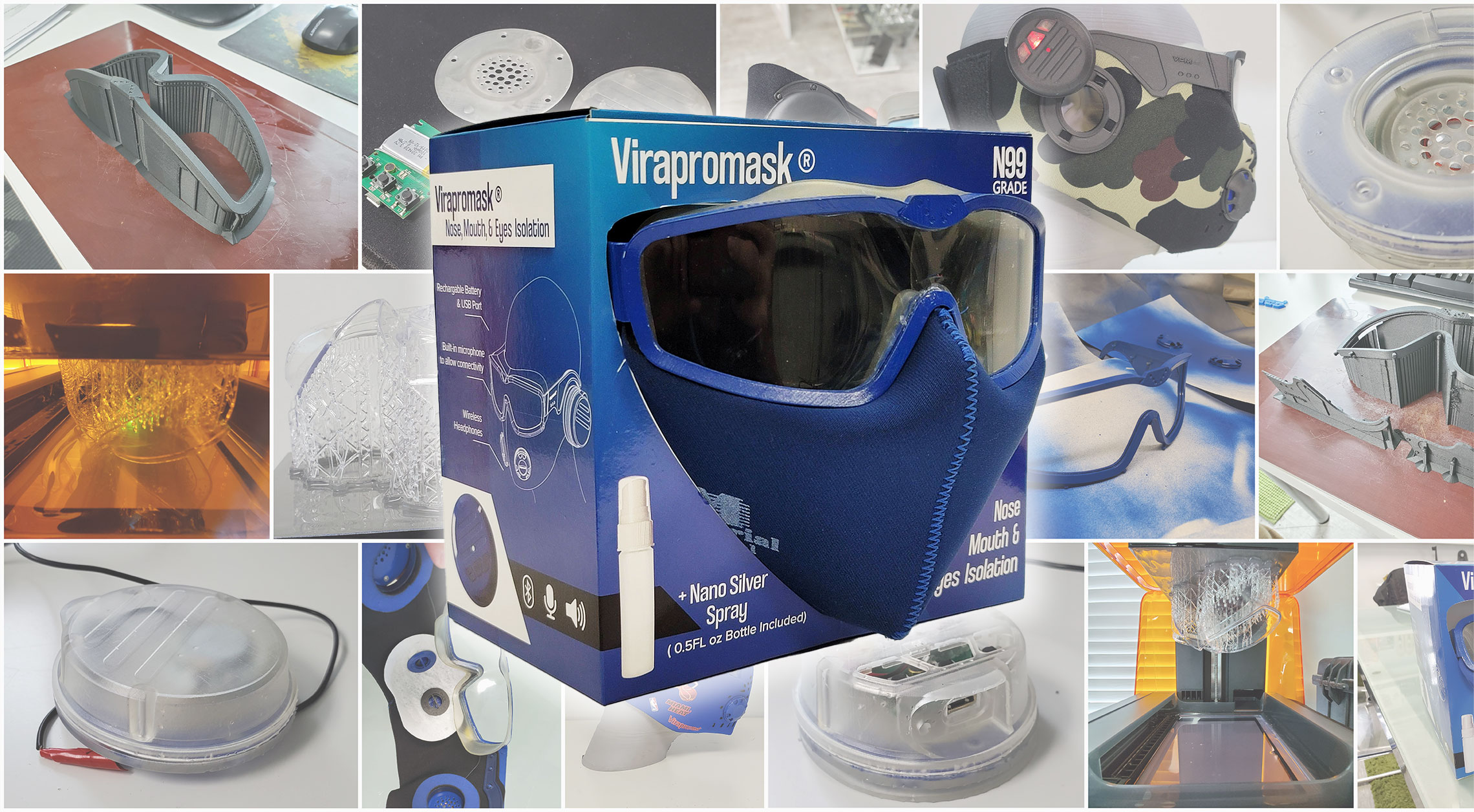
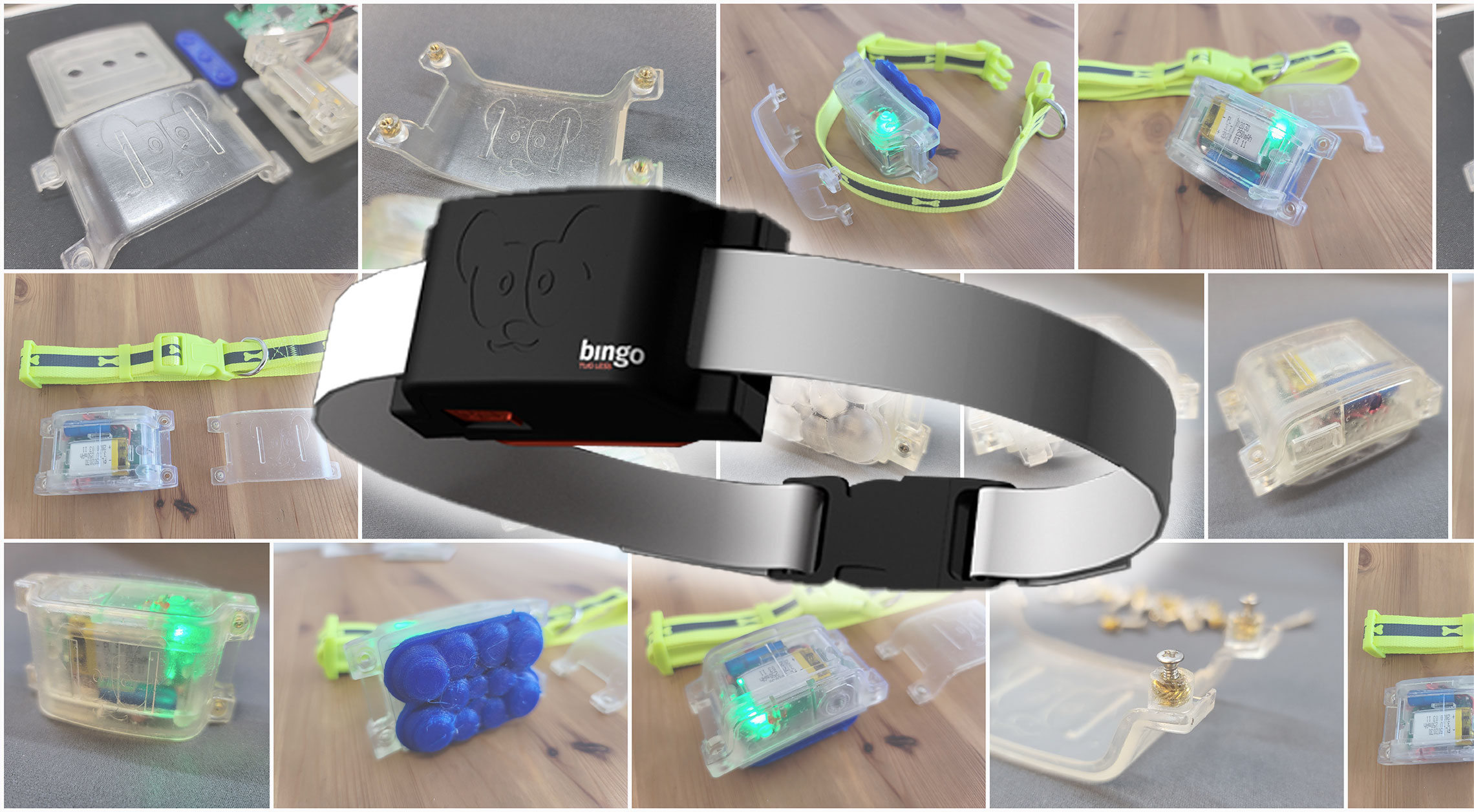
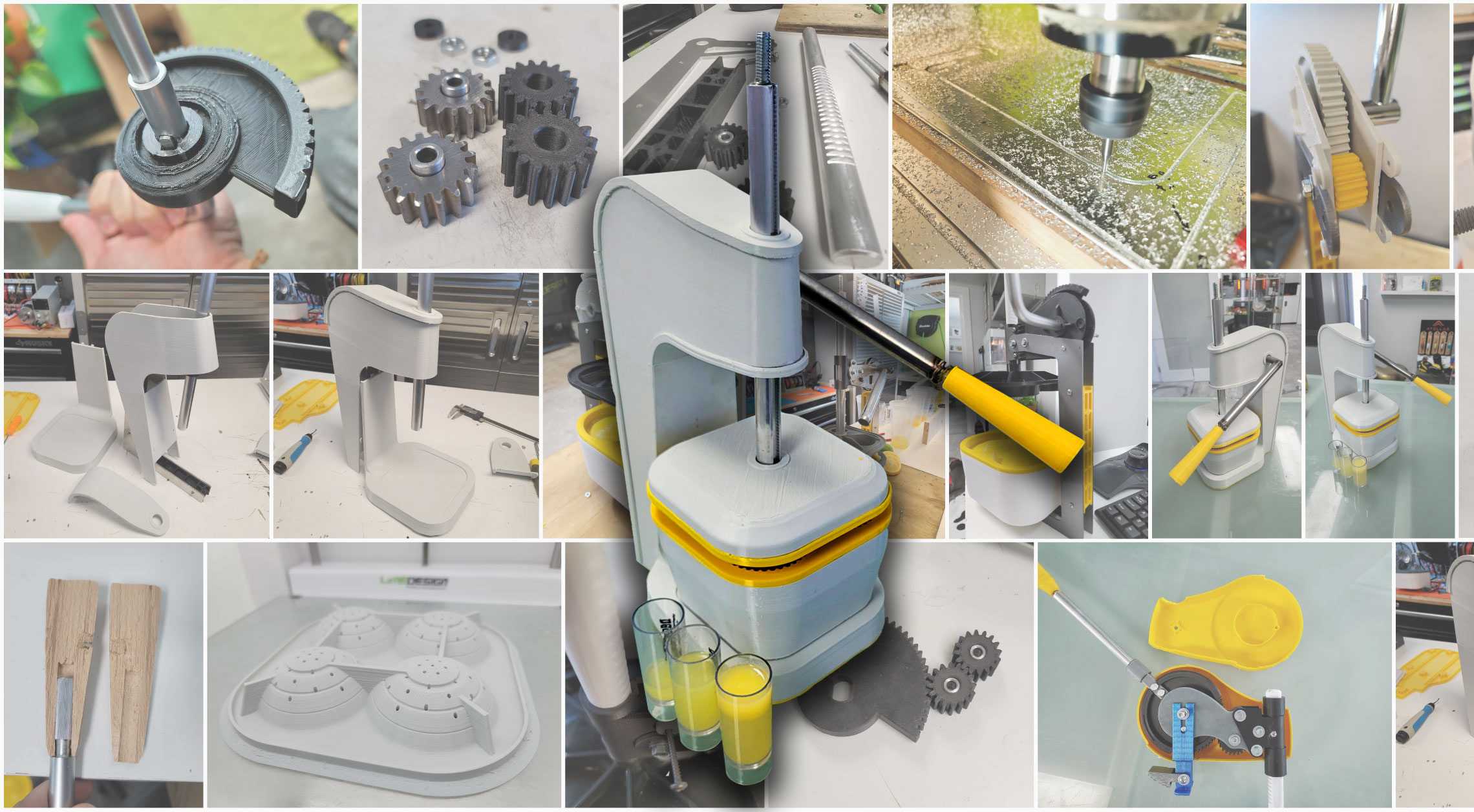



Prototyping is a vital step in the Product Development Process. It allows designers and developers to test and refine their ideas before investing in full-scale production. By creating a prototype, the team can evaluate the design’s usability, identify potential issues, and make improvements before moving on to the production phase. Prototyping also provides valuable feedback from users, allowing the team to refine the design and improve the user experience. This feedback can then be incorporated into the final product, increasing its chances of success. Ultimately, prototyping is a critical step in the product development process as it minimizes risks and maximizes the potential for success.

“Prototyping is the bridge between imagination and reality in product development.” Prototyping is like a blueprint for a building. Just as a blueprint provides a detailed plan for a construction project, a prototype serves as a tangible representation of an idea in product development. Without a blueprint, a building may collapse or fail to meet the owner’s expectations. Similarly, without a prototype, a product may not function properly or meet the user’s needs. Prototyping is essential for bridging the gap between imagination and reality in product development.
Founder and CEO – Rodrigo Lima
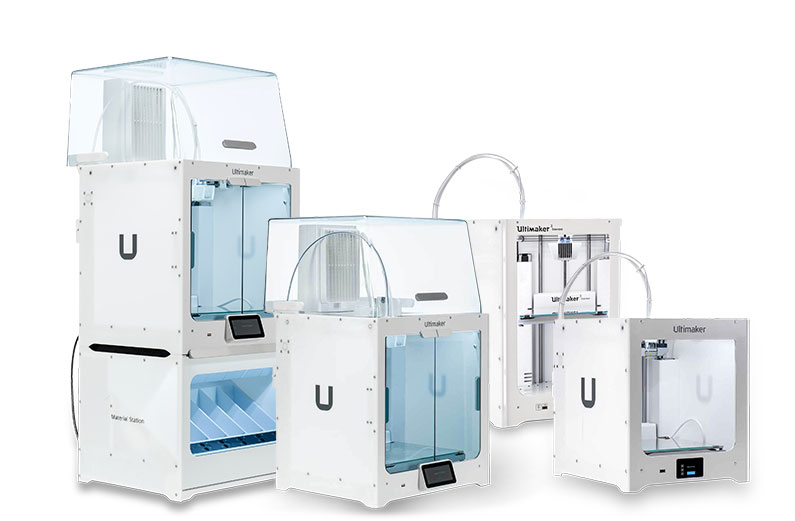
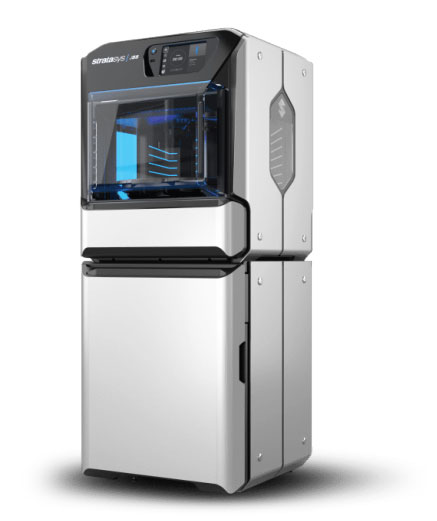






Now that we have gone through the previous phases and created the necessary guidelines for how the product should be, we can begin building physical prototypes. The goal for an Alpha prototype is not to create a beautiful final version of the product. The Alpha prototype is designed to test, early in the design process, the fundamental technologies upon which the product is based. We develop our Alpha prototypes by 3D printing the mechanisms and housing, and breadboards for electronics if needed. Using 3D printing is a fast way to create exactly what we need and the perfect way to ensure the dimensions of the product are what we need. We have incredible state-of-the-art 3D printers.
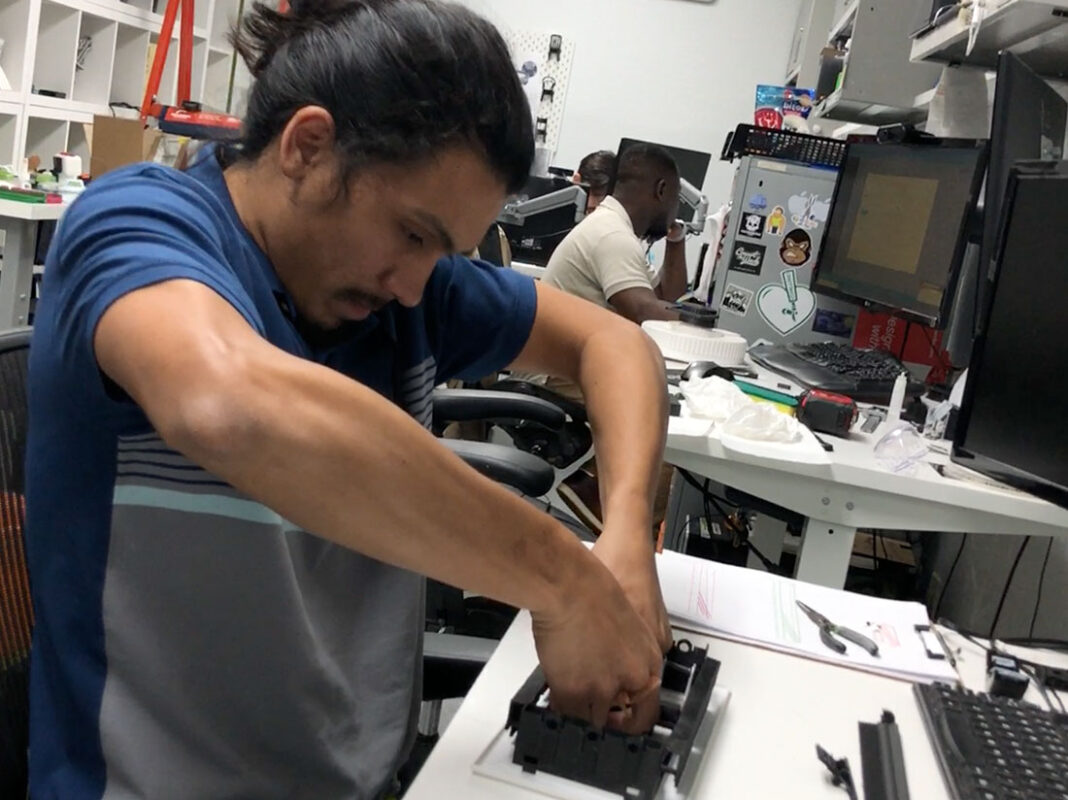

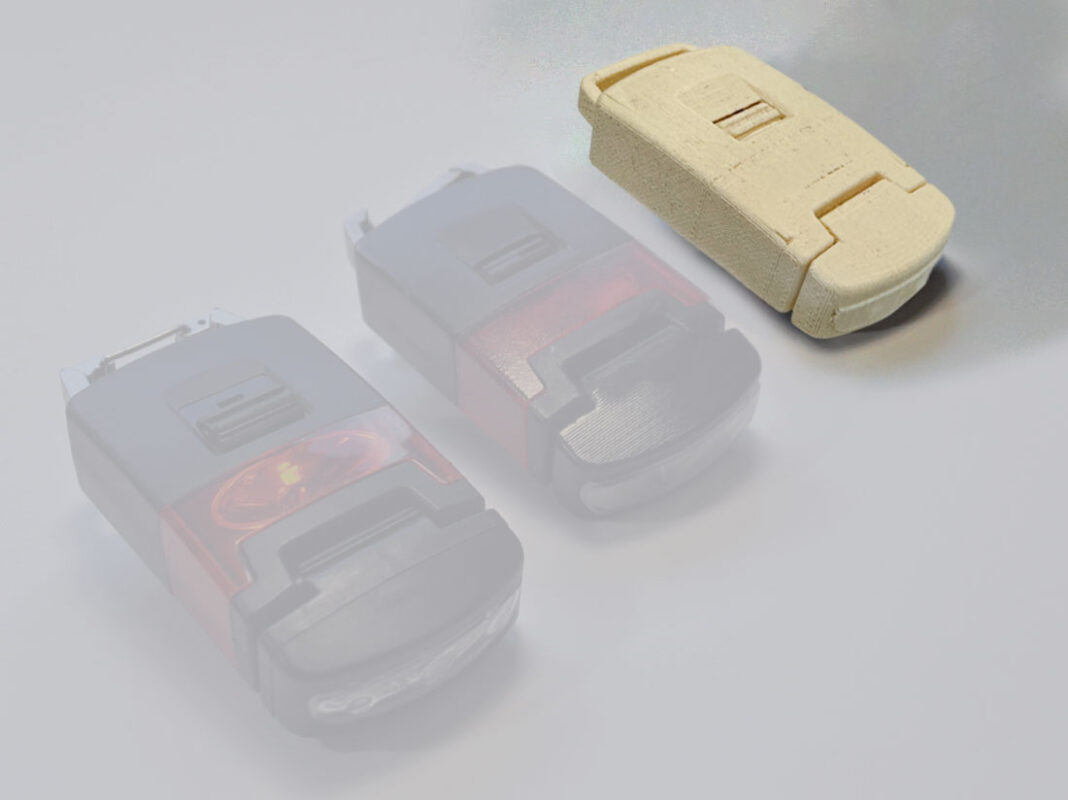
Reviewing and assessing the initial alpha prototype is a crucial step in the product development process. The prototype should be tested for functionality and usability to identify any flaws or areas for improvement. It’s important to gather feedback to ensure that the prototype meets the desired goals and objectives. Based on the feedback received, changes and refinements may need to be made to the design, features, materials, or other aspects of the prototype. Their may need to be more than one round of alpha prototyping through the same process of testing and feedback until it meets the desired standards and is ready to move forward to the next stage of development.
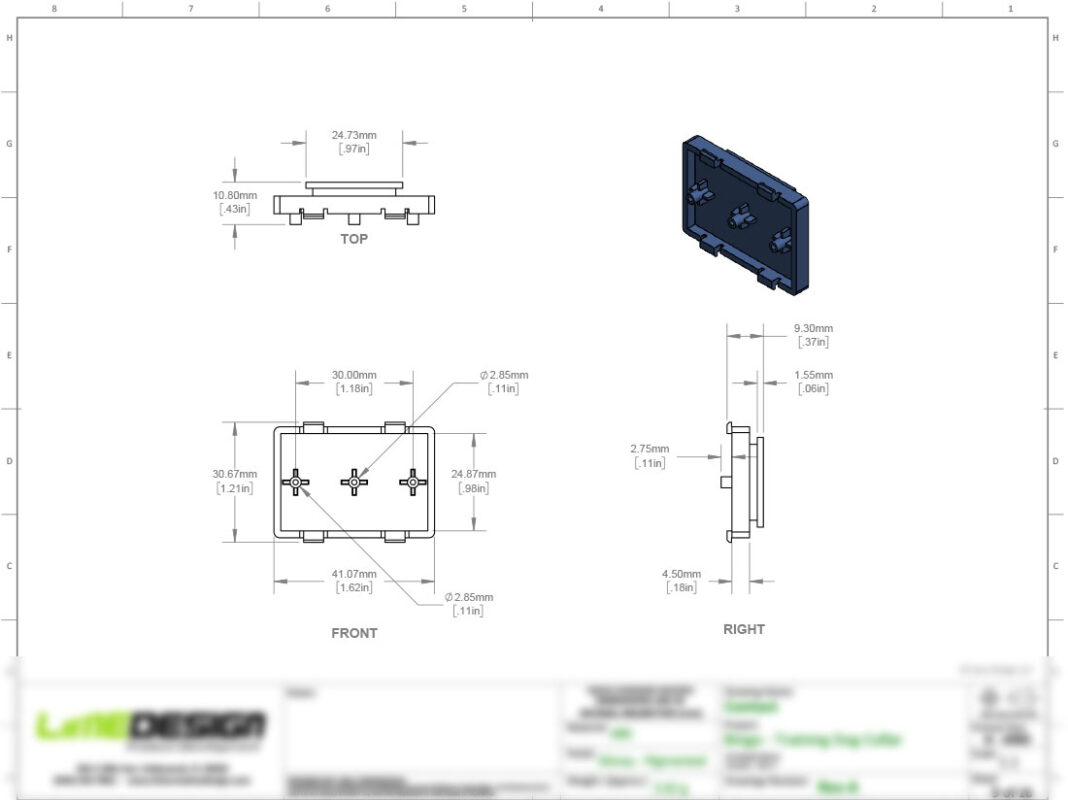
After making engineering refinements to the alpha prototype and creating a new alpha prototype, it’s important to update the technical drawings of the product. Documenting each iteration of the product is essential because it provides valuable references for future design updates or modifications. The tech drawings serve as a blueprint for the manufacturing process and provide a detailed illustration of the product’s design and specifications. Technical drawings may need to be revised to reflect changes in the design, dimensions, materials, or other specifications.
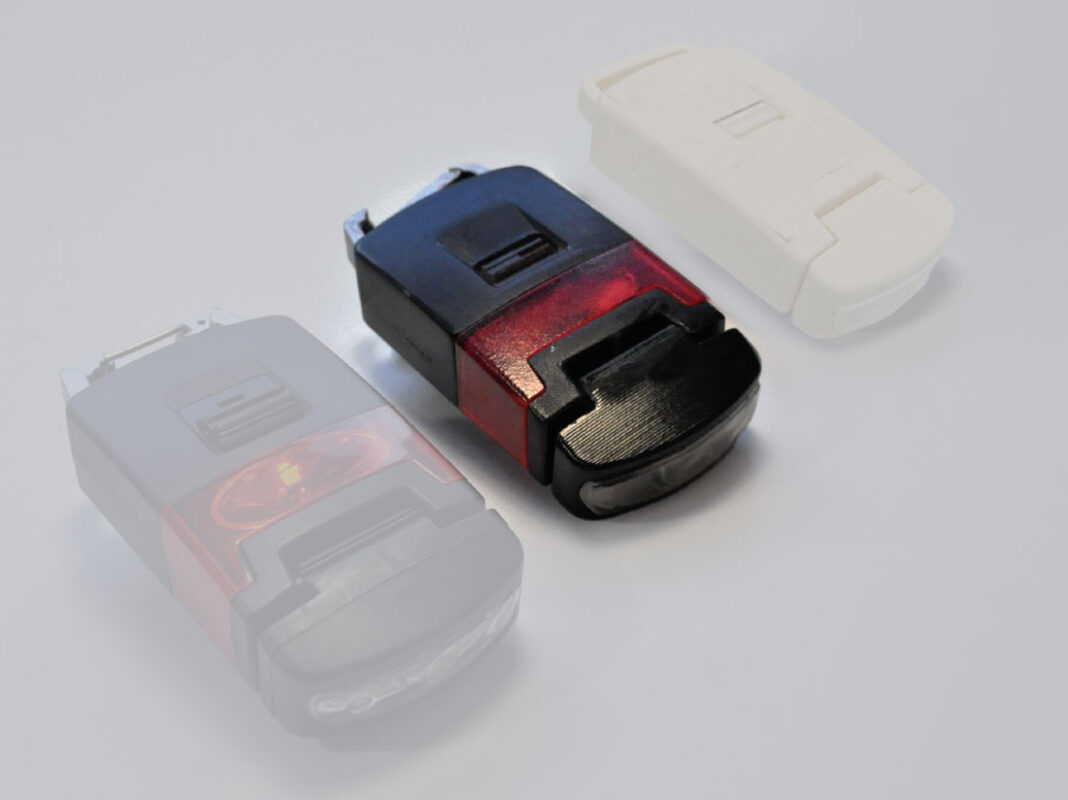

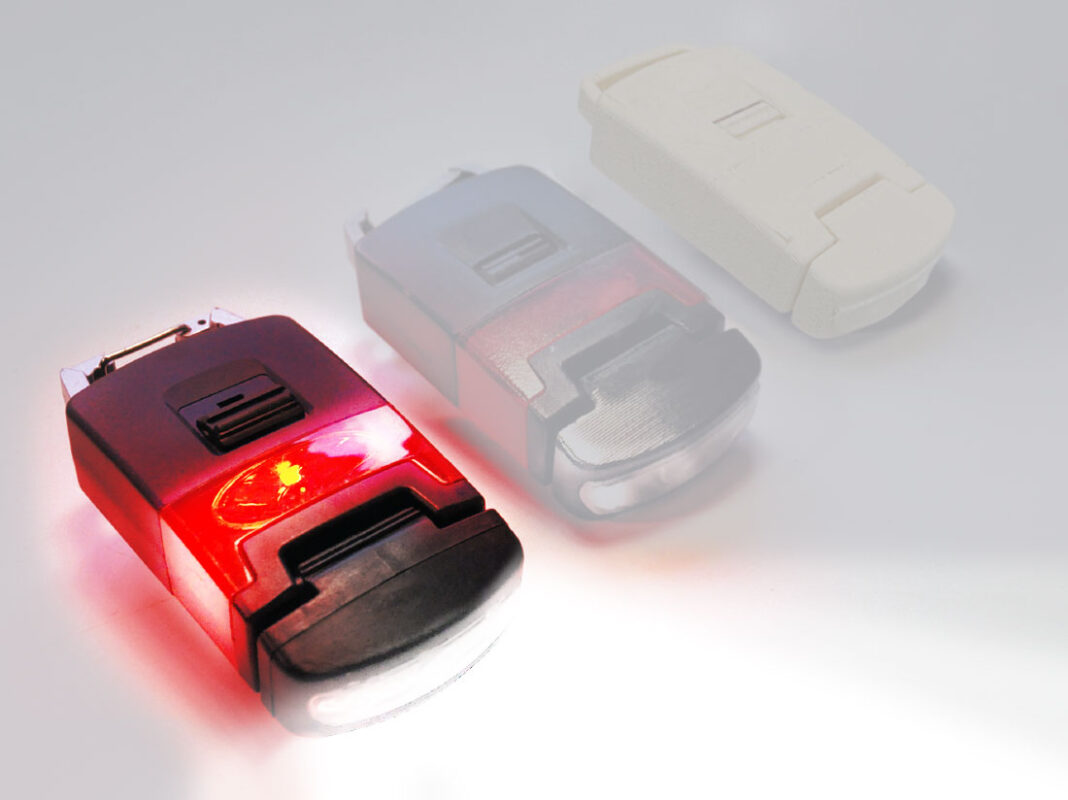
Creating a beta prototype involves further development and refinement of the product after the alpha prototype has been tested and validated. The process begins with incorporating feedback from our reviews on the alpha prototype to refine and improve the design. Then the beta prototype is built using more advanced materials or components to further test and refine the product’s functionality and features. Once the beta prototype has been thoroughly tested and refined, it can be used to develop a final version of the product for commercialization or production. Beta prototypes can also be used for marketing material as this will be a high quality prototype that looks as close as possible to how the final production product will look.

Once the Beta prototype phase is finished and we have a final prototype we are happy with, we move onto getting a sample from a factory. The Pilot sample is a small batch of products that are produced by a manufacturer to test the production process, quality, and performance of a product before proceeding with full-scale production. The pilot sample can be created as part of a product development process, or as a test run before ramping up to full production. The results of testing the pilot sample may lead to adjustments in the design or production process, to ensure that the final product meets the desired quality and performance standards.
Choose your path and either decide to go down the path of Manufacturing or Licensing your product. If you want to pursue manufacturing, we will prepare a proposal for 3D modeling, engineering, prototyping, and manufacturing for your product. If you want to pursue licensing, we will prepare a proposal for us to help you create marketing tools such as 3D modeling, animation, and presentations – which will help give you the tools to license your idea or try to raise funding from investors to further develop your idea.
Prototyping is crucial as it allows designers and engineers to visualize and test product concepts before full-scale production. It helps identify design flaws, refine functionalities, and gather valuable feedback from stakeholders and end-users early in the development process. By iterating on prototypes, teams can mitigate risks, improve user experience, and ultimately create more successful and market-ready products.
We offer a range of prototyping services tailored to meet diverse project needs. These include rapid prototyping using 3D printing technology, functional prototypes for testing mechanical and electronic components, and visual prototypes for showcasing design concepts. We also specialize in iterative prototyping to facilitate continuous refinement and optimization throughout the product development lifecycle
The time required to create a prototype depends on various factors such as the complexity of the product, the chosen prototyping method, and the availability of resources. Simple prototypes can be developed in a matter of days, while more intricate designs may take several weeks to manufacture and assemble. Effective project planning, clear communication, and efficient collaboration among team members are essential for ensuring timely prototyping and iterative refinement.
Are you an inventor with a groundbreaking idea, but unsure of how to turn it into a reality? Look no further! Our product development firm specializes in partnering with inventors like you to bring innovative concepts to market.
Let us be your trusted partner in transforming your vision into a tangible product that revolutionizes the market. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and take the first step towards making your idea a success!
Thank you for showing interest in Lime Design, you can fill out the contact form below and tell us a little about your project and we will contact you to setup a discovery meeting to give you an accurate quote.
Upon completing this form you will be emailed an NDA (mutual non-disclosure agreement), please sign it as soon as you can.


English, Spanish, Portuguese
Copyright @ 2008-2023 | All Rights Reserved | Terms & Conditions

English, Spanish, Portuguese
Copyright @ 2008-2023 | All Rights Reserved | Terms & Conditions